本文分析,当我们使用qemu-system-x86_64 --enable-kvm命令运行虚拟机的时候,QEMU与KVM是如何共同工作的。
本文分析/dev/kvm支持的IOCTL – KVM_CREATE_VM
1. QEMU
在qemu/accel/kvm/kvm-all.c文件中的kvm_init()函数中有1
2
3do {
ret = kvm_ioctl(s, KVM_CREATE_VM, type);
}while (ret == -EINTR)
其会对/dev/kvm的设备不停地调用KVM_CREATE_VM ioctl来创建一个VM。
2. KVM
在linux/virt/kvm/kvm_main.c文件中有kvm_dev_iotctl()函数用来处理userspace对/kvm/dev设备进行的ioctl操作。
其对KVM_CREATE_VM的操作的处理函数为kvm_dev_ioctl_create_vm()。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45static int kvm_dev_ioctl_create_vm(unsigned long type)
{
int r;
struct kvm *kvm;
struct file *file;
kvm = kvm_create_vm(type);
if (IS_ERR(kvm))
return PTR_ERR(kvm);
r = kvm_coalesced_mmio_init(kvm);
if (r < 0)
goto put_kvm;
r = get_unused_fd_flags(O_CLOEXEC);
if (r < 0)
goto put_kvm;
file = anon_inode_getfile("kvm-vm", &kvm_vm_fops, kvm, O_RDWR);
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
put_unused_fd(r);
r = PTR_ERR(file);
goto put_kvm;
}
/*
* Don't call kvm_put_kvm anymore at this point; file->f_op is
* already set, with ->release() being kvm_vm_release(). In error
* cases it will be called by the final fput(file) and will take
* care of doing kvm_put_kvm(kvm).
*/
if (kvm_create_vm_debugfs(kvm, r) < 0) {
put_unused_fd(r);
fput(file);
return -ENOMEM;
}
kvm_uevent_notify_change(KVM_EVENT_CREATE_VM, kvm);
fd_install(r, file);
return r;
put_kvm:
kvm_put_kvm(kvm);
return r;
}
可以看到,kvm_dev_ioctl_create_vm()函数主要做了以下几件事:
- kvm_create_vm();
- kvm_coalesced_mmio_init();
如果支持kvm_mmio,那么初始化对应的mmio. - create a fd for the creating VM and hooking it up to an anonymous inode;
为该VM创建一个匿名的fd,方便userspace使用该fd来进行该vm相关的ioctl(vcpu,msr,cpuid等设置vcpu_run)。 - kvm_create_vm_debugfs();
在debug filesystem 的/sys/kernel/debug/kvm为该VM动态创建一个task_pid-fd的文件夹,以及该VM相关的stat的文件。初始化该VM相关的debugfs。 - kvm_uevent_notify_change();
2.1 kvm_create_vm() – virt/kvm/kvm_main.c
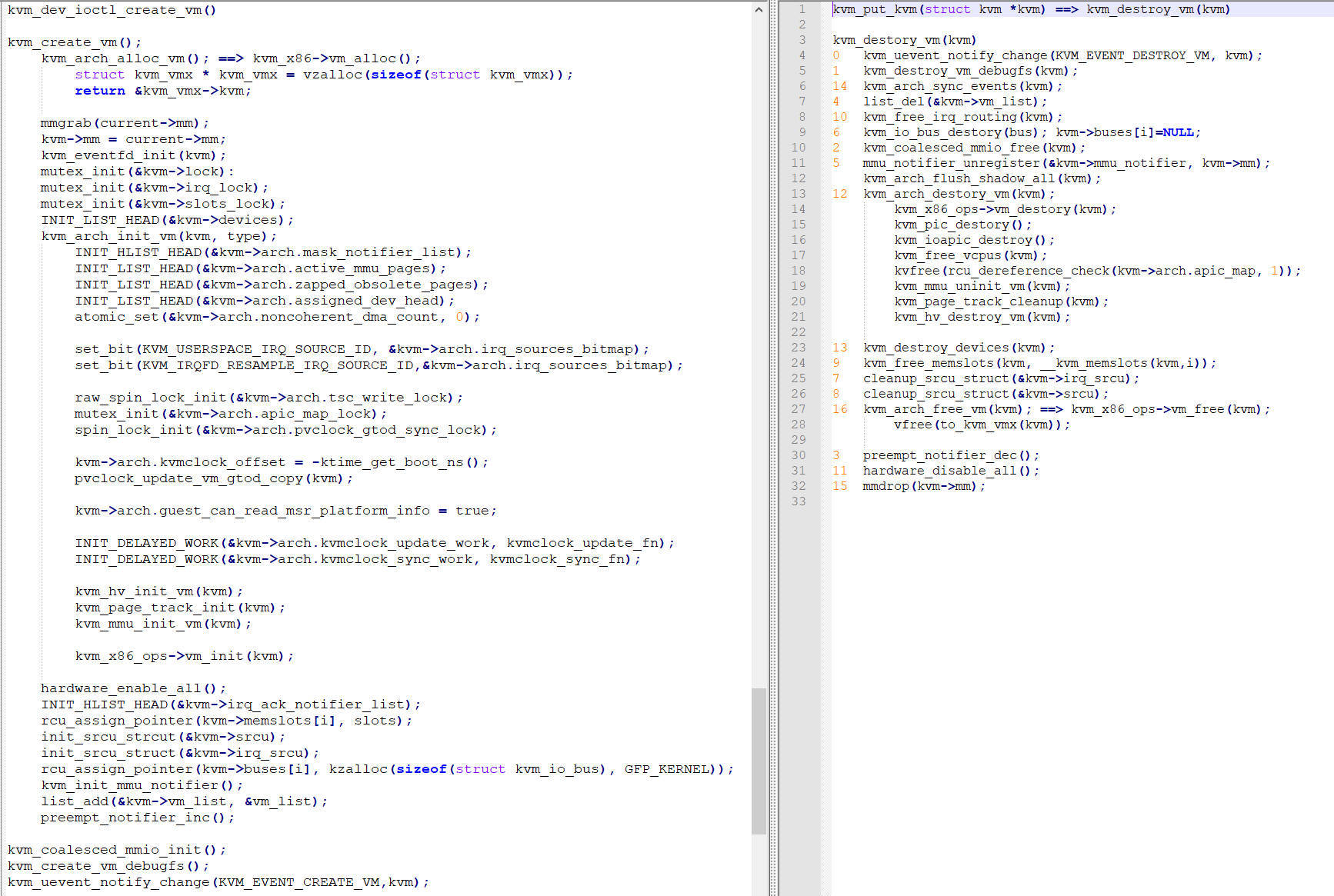
下面我们来分析第一步kvm_create_vm()函数主要做了什么:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84static struct kvm *kvm_create_vm(unsigned long type)
{
int r, i;
struct kvm *kvm = kvm_arch_alloc_vm();
if (!kvm)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
spin_lock_init(&kvm->mmu_lock);
mmgrab(current->mm);
kvm->mm = current->mm;
kvm_eventfd_init(kvm);
mutex_init(&kvm->lock);
mutex_init(&kvm->irq_lock);
mutex_init(&kvm->slots_lock);
refcount_set(&kvm->users_count, 1);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kvm->devices);
r = kvm_arch_init_vm(kvm, type);
if (r)
goto out_err_no_disable;
r = hardware_enable_all();
if (r)
goto out_err_no_disable;
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kvm->irq_ack_notifier_list);
BUILD_BUG_ON(KVM_MEM_SLOTS_NUM > SHRT_MAX);
r = -ENOMEM;
for (i = 0; i < KVM_ADDRESS_SPACE_NUM; i++) {
struct kvm_memslots *slots = kvm_alloc_memslots();
if (!slots)
goto out_err_no_srcu;
/*
* Generations must be different for each address space.
* Init kvm generation close to the maximum to easily test the
* code of handling generation number wrap-around.
*/
slots->generation = i * 2 - 150;
rcu_assign_pointer(kvm->memslots[i], slots);
}
if (init_srcu_struct(&kvm->srcu))
goto out_err_no_srcu;
if (init_srcu_struct(&kvm->irq_srcu))
goto out_err_no_irq_srcu;
for (i = 0; i < KVM_NR_BUSES; i++) {
rcu_assign_pointer(kvm->buses[i],
kzalloc(sizeof(struct kvm_io_bus), GFP_KERNEL));
if (!kvm->buses[i])
goto out_err;
}
r = kvm_init_mmu_notifier(kvm);
if (r)
goto out_err;
spin_lock(&kvm_lock);
list_add(&kvm->vm_list, &vm_list);
spin_unlock(&kvm_lock);
preempt_notifier_inc();
return kvm;
out_err:
cleanup_srcu_struct(&kvm->irq_srcu);
out_err_no_irq_srcu:
cleanup_srcu_struct(&kvm->srcu);
out_err_no_srcu:
hardware_disable_all();
out_err_no_disable:
refcount_set(&kvm->users_count, 0);
for (i = 0; i < KVM_NR_BUSES; i++)
kfree(kvm_get_bus(kvm, i));
for (i = 0; i < KVM_ADDRESS_SPACE_NUM; i++)
kvm_free_memslots(kvm, __kvm_memslots(kvm, i));
kvm_arch_free_vm(kvm);
mmdrop(current->mm);
return ERR_PTR(r);
可以看见kvm_create_vm()函数执行成功最终会返回struct kvm *的指针,执行不成功会返回一个error code。
Note:
struct kvm结构体为KVM中表示一个虚拟机VM的数据结构。
首先会调用
kvm_arch_alloc_vm()函数,动态分配struct kvm结构体,并返回其指针。
这里会肯定不同的arch有不同的实现,在x86 arch中会调用kvm_x86_ops->vm_alloc(),如果是Intel的CPU,那么会调用vmx_vm_alloc()函数:1
2
3
4
5static struct kvm *vmx_vm_alloc(void)
{
struct kvm_vmx *kvm_vmx = vzalloc(sizeof(struct kvm_vmx));
return &kvm_vmx->kvm;
}可以看到,其会动态分配一个vmx specific的结构体
struct kvm_vmx,其包含一个struct kvm,并返回其成员变量的指针&kvm_vmx->kvm。
即不同的x86架构在create vm的时候,需要自己specific的信息。- 当为VM动态分配了struct kvm结构后,会初始化该vm相关的一些结构变量(第9-17行)。
然后调用
kvm_arch_init_vm(kvm_type)函数,针对不同的arch(arm/x86/等)进行不同的初始化,我们只关心x86 arch的过程:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38int kvm_arch_init_vm(struct kvm *kvm, unsigned long type) //x86 arch
{
if (type)
return -EINVAL;
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kvm->arch.mask_notifier_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kvm->arch.active_mmu_pages);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kvm->arch.zapped_obsolete_pages);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kvm->arch.assigned_dev_head);
atomic_set(&kvm->arch.noncoherent_dma_count, 0);
/* Reserve bit 0 of irq_sources_bitmap for userspace irq source */
set_bit(KVM_USERSPACE_IRQ_SOURCE_ID, &kvm->arch.irq_sources_bitmap);
/* Reserve bit 1 of irq_sources_bitmap for irqfd-resampler */
set_bit(KVM_IRQFD_RESAMPLE_IRQ_SOURCE_ID,
&kvm->arch.irq_sources_bitmap);
raw_spin_lock_init(&kvm->arch.tsc_write_lock);
mutex_init(&kvm->arch.apic_map_lock);
spin_lock_init(&kvm->arch.pvclock_gtod_sync_lock);
kvm->arch.kvmclock_offset = -ktime_get_boot_ns();
pvclock_update_vm_gtod_copy(kvm);
kvm->arch.guest_can_read_msr_platform_info = true;
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&kvm->arch.kvmclock_update_work, kvmclock_update_fn);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&kvm->arch.kvmclock_sync_work, kvmclock_sync_fn);
kvm_hv_init_vm(kvm);
kvm_page_track_init(kvm);
kvm_mmu_init_vm(kvm);
if (kvm_x86_ops->vm_init)
return kvm_x86_ops->vm_init(kvm);
return 0;
}可见对于x86 arch而言,type必须为0。
- 然后初始化一些kvm->arch相关的结构。
- kvm_hv_init_vm(kvm);
- kvm_page_track_init(kvm);
- kvm_mmu_init_vm(kvm);
- 最后调用kvm_x86_ops->vm_init(kvm),进行特定的x86 arch(vmx/svm)相关的初始化。我们只关心intel cpu相关的vmx_vm_init():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32static int vmx_vm_init(struct kvm *kvm)
{
spin_lock_init(&to_kvm_vmx(kvm)->ept_pointer_lock);
if (!ple_gap)
kvm->arch.pause_in_guest = true;
if (boot_cpu_has(X86_BUG_L1TF) && enable_ept) {
switch (l1tf_mitigation) {
case L1TF_MITIGATION_OFF:
case L1TF_MITIGATION_FLUSH_NOWARN:
/* 'I explicitly don't care' is set */
break;
case L1TF_MITIGATION_FLUSH:
case L1TF_MITIGATION_FLUSH_NOSMT:
case L1TF_MITIGATION_FULL:
/*
* Warn upon starting the first VM in a potentially
* insecure environment.
*/
if (sched_smt_active())
pr_warn_once(L1TF_MSG_SMT);
if (l1tf_vmx_mitigation == VMENTER_L1D_FLUSH_NEVER)
pr_warn_once(L1TF_MSG_L1D);
break;
case L1TF_MITIGATION_FULL_FORCE:
/* Flush is enforced */
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
可见对于vmx而言,其初始化了kvm_vmx->ept_pointer_lock,并根据ple_gap更新kvm->arch.pause_in_guest的状态;最后根据打印一些CPU bug相关的warn信息到内核。
hardware_enable_all()
hardware_enable_all() -> on_each_cpu(hardware_enable_nolock) -> kvm_arch_hardware_enable()->
kvm_shared_msr_cpu_online();
kvm_x86_ops->hardware_enable() -> hardware_enable() vmx.c ->
kvm_cpu_vmxon(phys_addr); 在每个CPU上执行vmxon开启vmx支持。kvm_create_vm()函数然后初始化kvm->memslots[],kvm->srcu, kvm->irq_srcu, kvm->buses[], kvm_init_mmu_notifier(), kvm->vm_list, preempt_notifier_inc();